
Sequnential Logic System
alwasy @(posedge clk or negedge rst)
begin
if(rst == 0) begin
end
else begin
end
endalways구문-D F/F

module flip-flip(q,din,clk,rst);
input din, clk, rest;
output q;
reg q;
alwasy @(posedge clk or negedge rst)
begin
if(rst==0)
q<=0
else
q<=din;
end
endmodule| Combinational | Sequential |
| module combinational(a,b,sel,out); input a,b; input sel; output out; reg out; always @ ( a or b or sel) begin if (sel ) out=a; else out=b; end endmodule |
module sequential ( a, b, sel, clk, out); input a, b; input sel, clk; reg out; always @( posedge clk) begin if(sel) out<=a; else out <= b; end endmodule |
Combinational logic은 always 구문에서 입력에 따라 오퍼레이션이 달라지게 되고 Sequntial logic은 clk이 바뀜에 따라 달라진다.
assignment
1. Blocking assignment
evaluation, asignment가 즉시 이루어진다. = 가 사용된다.
| x = a | b; y = a^b^c; |
module blokcing (in,clk, out);
input in,clk;
output out;
reg q1, q2, out;
always @ (posedge clk)
begin
q1 = in;
a2 = q1;
out=q2;
end
endmodule
∴Combinational Logic에서는 Blocking assignment를 사용해야한다.
2. Nonblocking assignment
right-hane side가 evaluated 될 때 까지 모든 assignments가 연기된다.
module nonblocking(in,clk,out);
input in, clk;
output out;
reg q1, q2, out;
always @(posedge clk)
begin
q1<=in;
q2<=q1;
out<=q2;
end
endmodule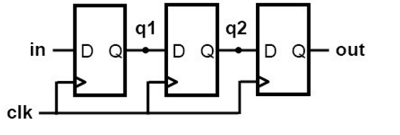
∴ sequential alsways blocks을 사용하기 위해서는 nonblocking assignment를 사용해야한다.
Combinatinal logic에 사용할 경우 deffer(연기)가 생김.
4-to-2 Binary Encoder
쓸데없는 우선 순위가 생기지 않게 유의해야 한다.
module binary_encoder(i,e);
input[3:0] i;
output[1:0] e;
reg e;
always @(i)
begin
if (i == 4'b0010) e = 2'b00;
else if ( i == 4'b0010 ) e = 2'b01;
else if( i == 4'b0100) e =2'b10;
else if ( i== 4'b1000) e = 2'b11;
else e = 2'bxx;
end
endmodulemutually exclusive condition 으로 코드를 짜야한다.
Code Example
D latch
module D_latch (D, Clk, Q);
input D, Clk;
output reg Q;
always @(D, Clk)
if(Clk)
Q=D;
endmoduleD F/F
1)
module D_FF (D, Clk, Q);
input D, Clk;
output reg Q;
always @(posedge Clk)
Q<=D;
endmodule2) blocking

module D_FF(D,Clk,Q1,Q2);
input D,Clock;
output reg (Q1,Q2);
always @(posedge Clok)
begin
Q1=D;
Q2=Q1; //D=Q1=Q2
end
endmodule3)NON- blocking

module D_FF(D,Clk,Q1,Q2);
input D,Clock;
output reg (Q1,Q2);
always @(posedge Clok)
begin
Q1<=D;
Q2<=Q1; //독립적인 FF
end
endmodule3)NON- blocking+RESET
asynchronous reset
module D_FF(D,Clk,Resetn,Q);
input D,Clock,Resetn;
output reg Q;
always @(negedge Resetn,posedge Clok)
if(!Resetn)
Q<=0;
else
Q<=D;
endmoduleclock에 상관없이 resetn에도 반응
synchronous reset
module FF(D,Clk,Resetn,Q);
input D,Clk, Resetn;
output reg Q;
always @(posedge Clk)
if(!Resetn)
Q<=0;
else
Q<=D;
endmoduleresetn이 clock에 반응하여 작동
'학사_공부 정리 > 디지털논리회로' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [ Verilog ] 베릴로그 기본 (0) | 2022.12.05 |
|---|